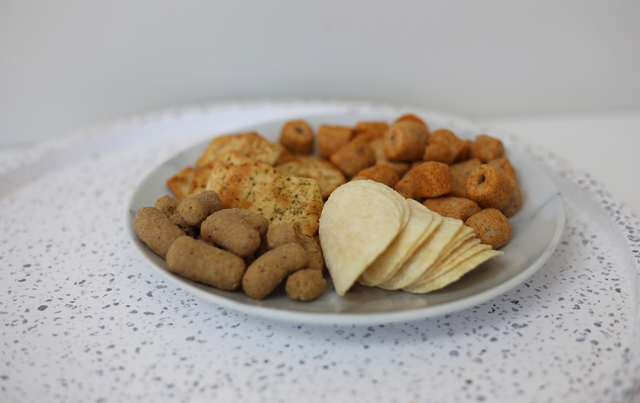
Research from Deakin University has suggested most Australian children are at risk of developing high blood pressure at a younger age due to eating too much salt.
In a new study produced by researchers from Deakin’s Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, cross-sectional analysis of 755 Victorian schoolchildren aged 4 to 12 found three quarters of children exceeded the recommended upper level of sodium intake.
Combined with a lack of potassium, an important nutrient for balancing the effect of salt in the body, a fifth of the children in the study’s sample had elevated blood pressure.
Research lead Dr Carley Grimes said while high blood pressure was often seen as an adult problem, the study showed risk factors started early in childhood.
“High blood pressure in childhood can lead to heart problems later in life, so prevention needs to start early,” she.
“We found that in some groups of children, especially girls and children living with obesity, higher salt intake was linked to raised blood pressure.
“A child’s sex and body weight may influence how salt intake affects blood pressure, and these groups may be more sensitive to the effects of salt, but we need further research to better understand these differences.”
Children involved in the study came from across Victoria; from city and regional areas and from public and private schools.
Salt and potassium intake was measured via 24-hour urine collection, while blood pressure measurements used standard methods.
“We found nearly 1 in 5 children – 17% – had higher than normal blood pressure,” Dr Grimes said.
“High blood pressure is generally diagnosed over several clinical visits, so these findings are not a diagnosis, but they do suggest that raised blood pressure is present in some primary school aged children and could pose a future health risk.
“Policymakers can use this evidence to strengthen school canteen guidelines and policies aimed at reducing sodium in processed and packaged foods. Families and schools can help by reducing the availability of salty foods and encouraging children to eat more fruits and vegetables, which boost potassium.
“By lowering children’s salt intake, these strategies could help support healthier blood pressure as children grow, especially when combined with efforts to promote healthy weight.”
Visit nature.com/articles/s41440-025-02489-1 to view the study Sodium, Potassium and Blood Pressure in Australian Schoolchildren.